Parotid tumors
Parotid tumors are growths of cells that start in the parotid glands.
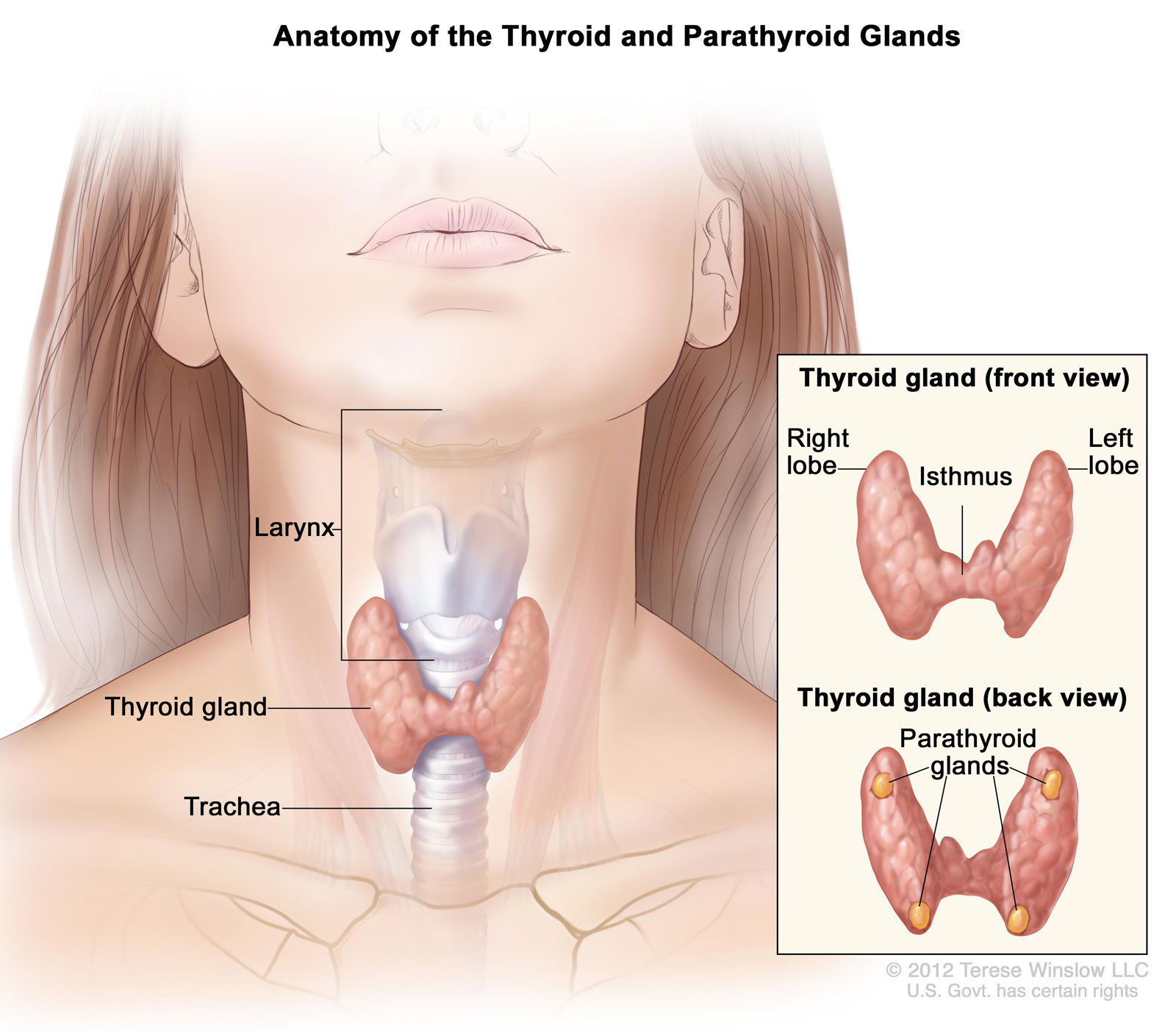
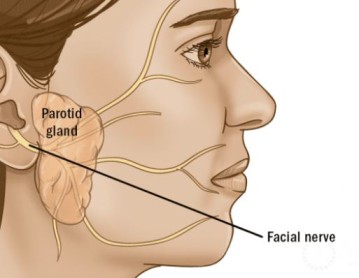
The parotids are two salivary glands that sit just in front of the ears. There is one on each side of the face. The salivary glands produce saliva to help with chewing and digesting food.
There are many salivary glands in the lips, cheeks, mouth, and throat. Cell growths, called tumors, can occur in any of these glands. The parotid glands are the most common place where salivary gland tumors occur.
Most parotid tumors are not cancerous. These are called noncancerous or benign parotid tumors.
Sometimes the tumors are cancerous. These are called malignant parotid tumors or parotid gland cancers.
Parotid tumors often cause swelling in the face or jaw. They often do not cause pain. Other symptoms include trouble swallowing or loss of facial movement.
Parotid Tumors – Diagnosis
Tests and procedures used to diagnose a parotid tumor may include:
Physical exam. Feeling the jaw and neck for lumps or swelling.
Biopsy. This is a procedure to collect a sample of tissue for examination. It usually involves using a needle to collect fluid or tissue from the parotid gland. The needle may be inserted through the skin on the face and the parotid gland. The results from a needle biopsy are not always correct. Sometimes the results say that a tumor is not cancerous when it is. For this reason, some doctors do not do a biopsy before surgery. Instead, they may take a sample of tissue for testing during surgery.
Imaging tests. Tests may include
⇒ultrasound,
⇒MRI, and
⇒CT scan.
Treatment
Treatment of a parotid tumor often involves surgery to remove the tumor. If the tumor is cancerous, you may need additional treatment. This could be radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Surgery
Surgeries used to remove parotid tumors include:
Removing part of the parotid gland. For most parotid tumors, surgeons can cut out the tumor and some of the healthy parotid tissue around it. The part of the parotid gland that is left continues to function as before.
Removing the entire parotid gland. Surgery to remove the entire parotid gland is called a parotidectomy. It may be needed for larger tumors, tumors that are cancerous, and those that affect deeper parts of the parotid gland.
Radiation therapy
Uses powerful beams of energy to kill cancer cells; the energy can come from sources such as X-rays and protons.
Radiation therapy is used to treat parotid cancer. Radiation therapy may be recommended after surgery.
If surgery is not possible, radiation therapy may be the first treatment for parotid cancer.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells. It is sometimes used to treat parotid cancer. It may be needed if there is a risk of the cancer spreading or if surgery is not an option. In these cases, chemotherapy may be given at the same time as radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy is sometimes used alone for advanced cancer, such as cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy can help relieve pain and other symptoms caused by cancer.