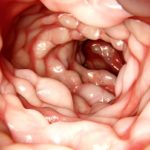
 Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the digestive tract that can affect any part of it. In most cases, it is located in the last part of the small intestine, in the ileum. Crohn’s disease affects all layers of the intestinal wall and there may be healthy parts of the intestine between the affected parts (partial enteritis). The disease affects the walls of the intestine with inflammation and ulcers causing abdominal pain and diarrhea in the patient.
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the digestive tract that can affect any part of it. In most cases, it is located in the last part of the small intestine, in the ileum. Crohn’s disease affects all layers of the intestinal wall and there may be healthy parts of the intestine between the affected parts (partial enteritis). The disease affects the walls of the intestine with inflammation and ulcers causing abdominal pain and diarrhea in the patient.
Frequency of occurrence
Young people between the ages of 16 and 35 have the highest incidence of Crohn’s disease, although people of any age can get the disease. It affects both men and women in similar percentages, while in many cases it is observed in people who have a family history of the disease. About 20% of people who present with the condition have a relative with a chronic inflammatory disease.
Crohn’s disease – Causes
The causes are not known, although the majority of research points to inflammatory, immunological, or even bacterial causes.
Unfortunately, a large percentage of patients, up to 70%, will need some form of surgery at some point.
Crohn’s disease – Symptoms
The main symptoms are abdominal pain, especially in the lower right abdomen, diarrhea, and weight loss. Patients with active Crohn’s disease often feel very tired and have a fever in outbreaks. The anemia they often present contributes to fatigue.
A small portion of patients suffers from the so-called extraintestinal manifestations of the disease, ie episodes or inflammations that affect the eyes, skin, mouth, joints, and spine.
Crohn’s disease – Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made mainly by colonoscopy (if the problem is in the large intestine or the final ileum), or by special imaging of the small intestine with magnetic resonance imaging (magnetic enterography) if the small intestine is affected. With the colonoscopy, the doctor is able to take small pieces of the intestine (biopsies) and send them for examination to the pathologist to confirm the diagnosis. Crohn’s disease can lurk in a young adult who experiences diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss, symptoms that can last for weeks or even months. Routine blood tests are likely to show anemia and general signs of inflammation.
Crohn’s disease is a chronic disease that presents with flares and relapses. This means that it is a condition that comes and goes, that is, a patient may be completely well for a long time, but at some point show recurrence and symptoms of the disease.
Once someone has an episode of the disease, it is almost certain that there will be another one in the future. How long someone will be completely well and when they will have a relapse can not be predicted. There are people who have few episodes in their lifetime, while some others, fortunately, few, have persistent symptoms.
Diet
It is essential for patients with Crohn’s disease to follow a balanced and proper diet, as the disease causes:
- anorexia
- reduced absorption of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals
- diarrhea
Although there are no specific foods that cause the symptoms to flare up, there are some foods that can help treat them:
- yogurt
- cheese
- almond milk
- eggs
- poultry
- fatty fish
- fruit and vegetables
- avocado
- cooked carrots
- potatoes
Life expectancy
When the symptoms of Crohn’s disease are detected early and treated appropriately, life expectancy does not differ from normal. However, frequent and systematic monitoring of the patient is important.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there is no definitive cure for Crohn’s disease. However, it is possible to satisfactorily control the disease with mainly pharmaceutical agents. There are a variety of drugs that help relieve symptoms in the acute phase of the disease as well as to maintain the remission intervals of the disease, ie the asymptomatic intervals. It should be noted that the medical treatment of Crohn’s disease must be completely individualized due to the wide range of manifestations of the disease in each patient. Conservative treatment of the disease should always be based on specialized gastroenterologists.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is the last resort in Crohn’s disease, however, it is necessary in case of complications of the disease, mainly obstruction or perforation. Laparoscopic treatment, although more demanding, is now possible in Crohn’s surgery as well. Other indications for surgery to treat Crohn’s disease:
- The creation of fistulas, ie communication resources between the intestine and the skin or other organs.
- Creating an abscess.
- The persistence of the disease despite medication, but without significant deterioration.
It is especially important for the patient to make the decision for surgical treatment at the right time. Surgical treatment at that stage is the only way to avoid much more serious complications and worsening of symptoms.
Surgery as a treatment for Crohn’s disease can and should be avoided, especially in the early stages of the disease, as available medications usually put the condition in remission for a long time.
Postponement of surgery when conservative measures fail to control the disease or its complications, significantly increases the morbidity of the disease.
Laparoscopic surgical treatment of Crohn’s disease
Laparoscopic surgery is, under certain conditions, an appropriate treatment option for Crohn’s disease, when surgery is necessary. It is an ideal choice in cases of small resections such as ileotyphlectomy for localized disease.
Advantages of laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgery for Crohn’s disease offers a number of benefits to the patient:
- the short duration of hospitalization
- minimal tissue damage
- quick recovery and return to daily activities/work
- fast recovery
- the better aesthetic result
- minimal postoperative pain





