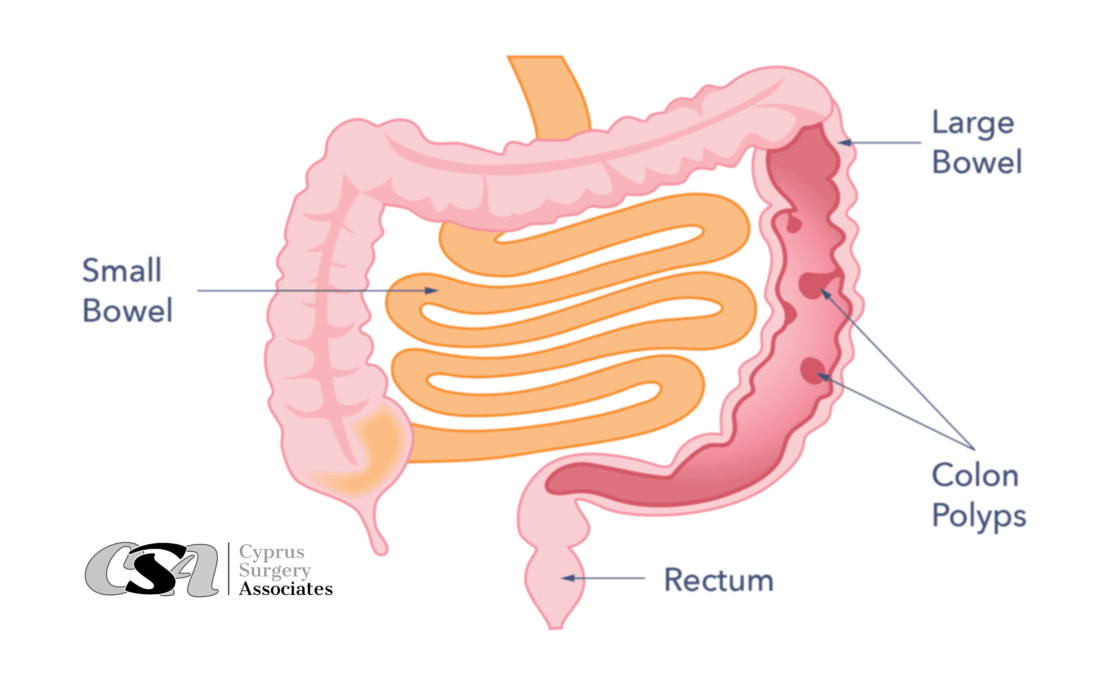
Colon polyps
Colon polyps are clumps of cells in the walls of the bowel. Most polyps are not dangerous. They tend to occur more often in people over 50, smokers, obese people, and those with a family history of bowel cancer.
A large percentage of adenomas (a type of polyp), if not diagnosed and treated immediately, can develop into cancer within 10 years. Therefore, a preventive colonoscopy is recommended every 5-10 years after the age of 50.
Types of polyps
Adenomas – benign tumors of the intestine, which can be asymptomatic. The larger in size and malformation they are, the more likely they are to develop into a malignancy. That is why it is recommended to remove them as a precaution.
Hyperplastic polyps – small polyps that usually do not develop into cancer.
Inflammatory polyps – found in people with inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, these are benign polyps that do not cause cancer.
Colon polyps – Symptoms
Polyps are usually asymptomatic (have no symptoms). However, when they do show signs and symptoms they are as follows:
- bleeding from the anus
- change in stool color
- blood in the stool
- diarrhea or constipation
- pain
- iron deficiency and anemia
The same symptoms may also indicate another condition, so it is not absolute that when you have these symptoms there is a polyp. They should just take you straight to the doctor for tests. The doctor responsible for the removal of polyps is the gastroenterologist and the general surgeon.
Colon – polyps – Diagnosis
Diagnosis plays a very important role as if they are not detected at an early stage and when they are small in size, they become dangerous. That is why it is recommended to have regular imaging tests such as colonoscopy so that they can be detected and removed completely and safely. Sigmoidoscopy and stool examination are also recommended.
Risk factors
- age (over 50),
- inflammatory bowel disease,
- family history,
- alcohol consumption,
- smoking, obesity,
- lack of physical exercise,
- race,
- and type II diabetes.
Colon polyps – Treatment
Treatment focuses on removing the polyp. The smaller it is, the safer and more effective it will be. It can be done by surgery and colectomy, by laparoscopy (a minimally invasive method of colectomy with very small incisions and immediate repair), and in cases where the polyps extend throughout the large intestine, colectomy and ileorectal or ileoanal anastomosis are recommended.
Some types of polyps are more likely to develop into cancer than others. Through the histological examination, it is detected whether the tissue is cancerous.
Of course, the most important role is played by post-operative follow-up, as the patient belongs to a high-risk group, and therefore, regular diagnostic tests (colonoscopy) are recommended at the intervals set by the doctor depending on the polyp that was identified and removed.