Gastric sleeve VS gastric bypass
Gastric sleeve and gastric bypass are weight loss surgeries that reduce the size of the stomach. There are several key differences in benefits, risks, and recovery.
Bariatric surgery is a procedure for weight loss. It is an option for obese individuals, especially if diet alone has not helped.
Two of the most common types of bariatric surgery are gastric sleeve surgery and gastric bypass surgery.
There are similarities and key differences between the two procedures.
Gastric Sleeve VS Gastric Bypass – Differences
Both gastric sleeve and bypass surgery reduce the stomach from its normal size into a small pouch. This causes weight loss in two ways:
1. The pouch fills up quickly, limiting the amount of food we can eat before we feel full.
2. Our bodies produce less ghrelin, commonly known as the “hunger hormone.”
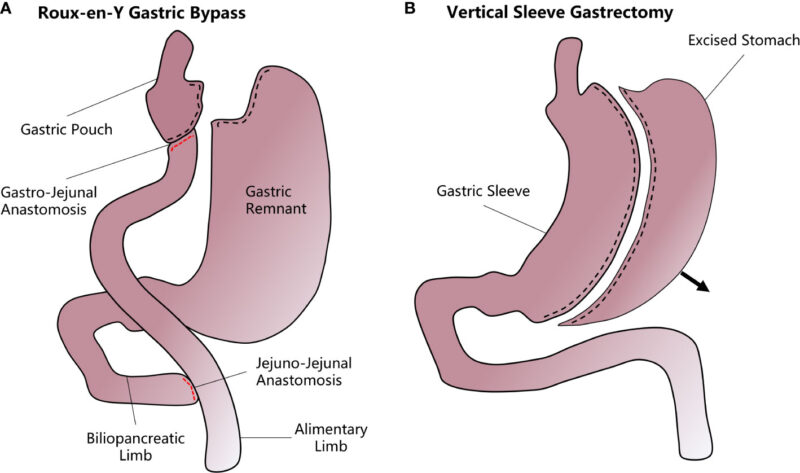
The methods differ in how the new stomach “sleeve” is created.
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
With gastric sleeve surgery, about 80% of the stomach is permanently removed.
What is left is shaped like a banana (or shirt sleeve). The digestive system does not undergo any other changes.
Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting the newly formed pouch directly to the small intestine. After gastric bypass, ingested food will enter this small stomach pouch and then directly into the small intestine, bypassing most of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine.
The part of the small intestine that is bypassed along with the stomach absorbs some nutrients and calories. Since food no longer passes through this part, these calories are not absorbed, contributing to weight loss.
This procedure is also called Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.
Is there a difference in recovery?
Gastric bypass surgery is more complicated than gastric sleeve surgery. Gastric sleeve surgery involves only one step, while gastric bypass is a two-step procedure.
Although gastric sleeve and gastric bypass surgery require similar hospital stays, gastric bypass has a longer overall recovery time. NHS Wales states that it can take 4 to 6 weeks to fully recover from gastric bypass surgery and 2 to 3 weeks to fully recover from gastric sleeve surgery.
Gastric Sleeve VS Gastric Bypass – Risks and Complications
Bariatric surgery is a relatively safe procedure.
According to the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), the risk of a major complication is around 4%. This is much lower than the risk of developing serious health problems related to obesity.
Some factors that can complicate any surgery, including bariatric surgery, include:
- bleeding
- deep vein thrombosis
- pulmonary embolism
- side effects of general anesthesia
- pneumonia
Potential complications after bariatric surgery include:
- cholelithiasis
- gastric fluid leakage
- nutritional deficiencies, including vitamin deficiencies
- Dumping syndrome (rapid gastric emptying)
Complications of gastric sleeve surgery
Complications associated with gastric sleeve surgery include:
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- stomach stricture
Complications of gastric bypass surgery
Specific complications of gastric bypass include:
- increased sensitivity to alcohol
- stomach perforation
- ulcer stomach
- intestinal obstruction
Dietary changes required
The dietary changes that will need to be made after these operations are generally the same.
According to the National Health Service (NHS):
You will only be given liquids for the first few days after the operation.
Shortly after, you will be able to eat pureed food and then soft food. You will continue this diet for 4 to 6 weeks after the operation.
Six weeks after the operation, you will be able to eat normal food.
Important dietary guidelines to follow after gastric sleeve or gastric bypass surgery include:
- eat small amounts and stop when you are full
- chew your food thoroughly
- eat slowly
- take recommended vitamins and supplements
- stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- avoid foods that are difficult to digest, such as tough meats and bread
- avoid carbonated beverages
The main difference after surgery is the size of your stomach pouch, which affects how much you can eat.
With gastric bypass, the pouch holds about 1 oz (ounce) of food, which is slightly smaller than a golf ball. Gastric sleeve surgery creates a pouch that holds 2 to 5 oz. of food.
Gastric Sleeve VS Gastric Bypass – Pros and Cons
According to the AMBS, about 90% of people who undergo bariatric surgery lose more than 60% of their excess body weight. They can maintain much of their weight loss long-term.
Success rates vary depending on the type of surgery.
A 2014 study focused on morbidly obese people who underwent bariatric surgery between 2008 and 2010. Researchers found that participants who underwent laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery lost, on average, 64.2% of their excess body weight after 6 months. During the same period, those who underwent laparoscopic gastric bypass lost, on average, 67.9% of their excess body weight.
A 2018 follow-up study looked at how much weight these same participants had lost 5 years after surgery. During that time, participants who had laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery lost an average of 59% of their excess body weight. Participants who had laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery lost an average of 64% of their excess body weight.
One of the biggest benefits of gastric sleeve and gastric bypass surgery is that they significantly reduce the risk of obesity-related conditions, such as:
- type 2 diabetes
- hypertension, or high blood pressure
- hyperlipidemia, or high cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- heart disease
- stroke
- fatty liver disease
- sleep apnea
- knee or hip pain
In many cases, bariatric surgery can also help improve physical function, mood, and quality of life. According to a 2019 study, patients have been shown to need fewer prescription medications over time. This can reduce healthcare costs, helping to save money.
Bariatric surgery could also reduce the risk of premature death.
On the other hand, bariatric surgery has risks that are important to consider.
Bariatric surgery can also affect nutrient absorption. Over time, this can lead to health problems such as anemia and osteoporosis[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
In conclusion
The type of bariatric surgery that is best for you will depend on several factors, including:
- Current weight
- Weight loss goal
- Medical history
- Pre-existing conditions health conditions
- Expectations
- Personal preference
Talk to a doctor about these factors and whether bariatric surgery is right for you.
They can help you determine your eligibility and which procedure may be the best option.