Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer.
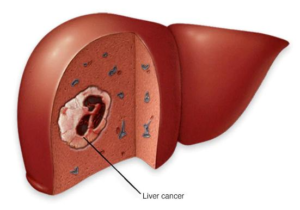
It occurs most often in people with chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection.
Risk factors
The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver cancer, is higher in people with long-term liver disease. It is also higher if the liver is scarred from infection with hepatitis B or hepatitis C.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is more common in people who drink large amounts of alcohol and have a buildup of fat in the liver.
Hepatocellular carcinoma – Diagnosis
Tests and procedures used to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma include:
- Blood tests to measure liver function
- Imaging tests, such as CT scans and MRIs
- Liver biopsy, in some cases, to remove a sample of liver tissue for laboratory testing
Hepatocellular carcinoma – Treatment
Which treatment is best depends on the size and location of the hepatocellular carcinoma and the patient’s overall health.
Treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma include:
Surgery.
Surgery to remove the cancer and a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it may be an option for people with early-stage liver cancer.
Liver transplant surgery.
Surgery to remove the entire liver and replace it with a liver from a donor may be an option in otherwise healthy people whose liver cancer has not spread beyond the liver.
Destroying cancer cells with heat or cold.
Ablation procedures to kill cancer cells in the liver using extreme heat or cold may be recommended for people who cannot have surgery. These procedures include radiofrequency ablation, cryoablation, and ablation using alcohol or microwaves.
Delivering chemotherapy or radiation directly to the cancer cells.
Using a catheter that is passed through blood vessels and into the liver, doctors can provide chemotherapy drugs (chemoembolization) or tiny glass spheres containing radiation (radioembolization) directly to the cancer cells.
Radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy using energy from X-rays or protons may be recommended if surgery is not an option. A specialized type of radiation therapy, called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), involves focusing multiple beams of radiation on one spot in the patient’s body at the same time.
Targeted drug therapy.
Targeted drugs may help slow the progression of the disease in people with advanced liver cancer.
Immunotherapy.
These drugs use the patient’s body’s immune system that fight germs to attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy may be an option for treating advanced liver cancer.





