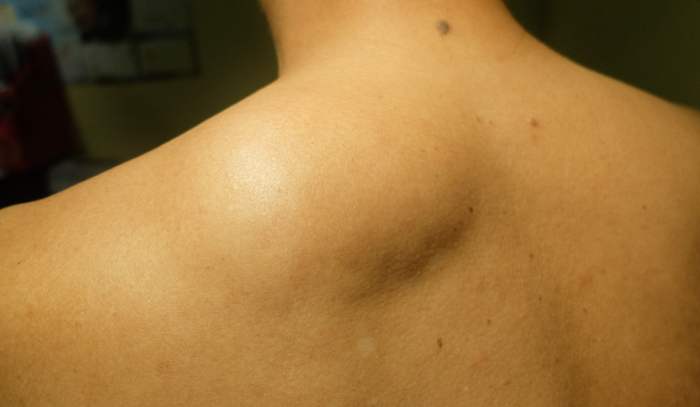
Liposarcoma
Liposarcoma is a rare type of cancer that starts in fat cells.
It most often starts as a growth of cells in the abdomen or the muscles of the arms and legs. However, liposarcoma can start in fat cells anywhere in the body.
It occurs most often in older adults but can occur at any age.
Its treatment usually involves surgery to remove the cancer.
Other treatments, such as radiation therapy, may also be used.
Liposarcoma is a type of cancer called soft tissue sarcoma. These cancers occur in the connective tissues of the body. There are many types of soft tissue sarcoma.
Liposarcoma – Symptoms
The symptoms depend on the part of the body where the cancer forms.
⇒Liposarcoma in the arms and legs can cause:
- A growing, palpable lump under the skin.
- Pain.
- Swelling.
- Weakness of the affected limb.
⇒Liposarcoma in the abdomen can cause:
- Abdominal pain.
- Abdominal swelling.
- Early satiety.
- Constipation.
- Blood in the stool.
Causes
It is not clear what causes liposarcoma.
Liposarcoma begins when fat cells get changes in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell the cell what to do. These changes turn fat cells into cancer cells by telling the cancer cells to grow quickly and make many more cells.
Cancer cells continue to live when healthy cells die as part of their natural life cycle.
The cancer cells form a growth, called a tumor. In some types of liposarcoma, the cancer cells continue to make more cells, causing the tumor to grow.
In other types of liposarcoma, the cancer cells may break off and spread to other parts of the body. When cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is called metastatic cancer.
Liposarcoma – Diagnosis
Tests and procedures used to diagnose liposarcoma include:
Imaging tests. Imaging tests create pictures of the inside of the body. They can help show the size of the liposarcoma. Tests may include X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Sometimes a positron emission tomography scan, or PET scan, is needed.
Biopsy. A procedure to remove some cells for examination. The sample may be removed with a needle passed through the skin. Or the sample may be taken during surgery to remove the cancer. The type of biopsy depends on the location of the cancer.
Liposarcoma – Treatment
Treatments for liposarcoma include:
Surgery. The goal of surgery is to remove the entire tumor.
If a liposarcoma grows and affects nearby organs, removing the entire tumor may not be possible.
In these cases, other treatments will be needed to shrink the liposarcoma. This will make it easier to remove during an operation.
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses powerful beams of energy to kill cancer cells; the energy may come from X-rays, protons, or other sources.
It may also be used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Radiation may also be used before surgery to shrink a tumor, making it more likely that the entire tumor will be removed.
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses strong drugs to kill cancer cells. Some chemotherapy drugs are given through a vein, and some are taken as pills.
Not all types of liposarcoma are sensitive to chemotherapy. Careful examination of the cancer cells can show whether chemotherapy is likely to help.
Chemotherapy may also be used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells. It may also be used before surgery to shrink a tumor. Chemotherapy is sometimes combined with radiation therapy.